Aortic aneurysm surgery
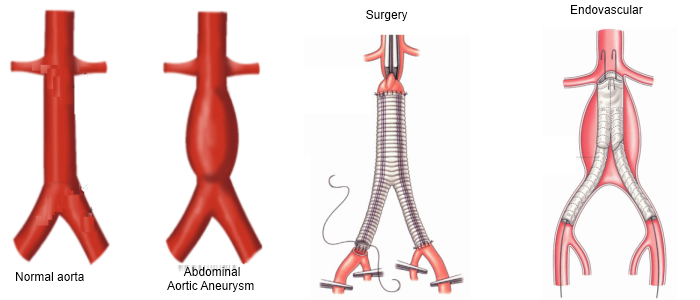
An aortic aneurysm is an abnormal enlargement, or bulging, of the wall of the aorta, the largest blood vessel in the body. As an aortic aneurysm grows, the walls of the aorta can be stretched thin, tense and weakened. If an aneurysm ruptures or tears, life-threatening internal bleeding can result.
Fortunately, if detected in time, an aneurysm may be repaired with traditional surgery or minimally invasive techniques. The best approach for repairing an aortic aneurysm is influenced by its location, size and physical condition.
The objective of aortic aneurysm surgery is to prevent the aneurysm from rupturing. The HonorHealth Aortic Program brings together an expert team of surgeons who specialize in performing a wide range of procedures, from traditional open surgery to less invasive approaches.
Traditional open surgery
Open surgery begins with a long incision in the chest or abdomen. Clamps are placed above and below the aorta to remove the diseased area. Then, the surgeon sews a synthetic tube or graft into the aorta in place of the removed section.
Endovascular aneurysm repair or endovascular stenting
This less invasive approach can be used in many but not all situations. Endovascular stenting doesn’t require a large incision and results in fewer perioperative complications and a shorter recovery time.
To perform endovascular stenting, catheters (thin, flexible tubes) are inserted through the groin, and a stent-graft — a woven tube surrounded and supported by a metal mesh which is compressed — is guided into the blood vessel to the site of the aortic aneurysm and deployed. These cases often require a specialized operating room that has high resolution X-ray equipment.
In effect, the stent-graft re-routes all the blood through its channel, which depressurizes the aneurysm and allows it to shrink in size.